Ventriculoperitoneal VP shunt surgery is a surgical procedure that involves draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the central nervous system in cases of hydrocephalus or excess pressure on the brain.
Acabar con el dolor es posible y nuestro equipo quiere ayudarle a conseguirlo. Dé el primer paso contactando con nosotros.
Madrid: +34 919 148 441
Barcelona: +34 936 090 777
Llevamos la excelencia neuroquirúrgica a Sevilla, ofreciendo servicios especializados en neurocirugía de columna y cráneo.
¡Llama al +34 955 277 751 o +34 633 143 686 para más información!
Ventriculoperitoneal VP shunt surgery is a surgical procedure that involves draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the central nervous system in cases of hydrocephalus or excess pressure on the brain.

This surgery is performed in cases of symptomatic hydrocephalus with the aim of draining the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid. In cases of acute hydrocephalus, there is no alternative treatment and delaying it can lead to reversible or even permanent brain damage to the patient. In cases of subacute or chronic hydrocephalus, and depending on the age of the patient, an endoscopic ventriculostomy can be considered as an alternative treatment.
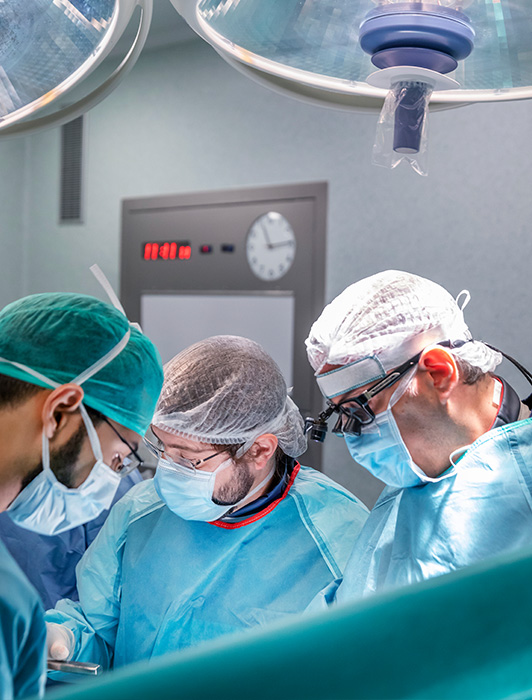
The surgery is performed in an operating room under general anesthesia. It involves placing a catheter, through a small hole, into a brain cavity called the ventricle, where the cerebrospinal fluid is housed.
This catheter is connected in series to a system with a valve to regulate the flow of CSF. Depending on the type of valve placed, the resistance to the passage of CSF through the system is greater or smaller. The catheter is tunneled under the skin, through the subcutaneous cellular tissue, from the head to the atrium or, more frequently, the peritoneum, where the cerebrospinal fluid is physiologically reabsorbed.
The recovery process varies according to the type of hydrocephalus the patient has.
Recovery depends a lot on the type of pathology that caused the hydrocephalus, usually it is a tumor or due to acute bleeding. Recovery will depend on the patient's previous neurological state.
Recovery is usually quick and the patient can be discharged from the hospital in 24-48 hours. The patient will undergo functional rehabilitation for walking and control of the sphincters. Patients and their families usually see significant improvement in walking by 1 to 3 months after the shunt placement surgery. The recovery of sphincter control and evolution of memory impairment are highly dependent on the patient's previous neurological state.
Like every surgery, there are some risks involved in a ventriculoperitoneal shunt:
Despite the possibility of some of these complications occurring, at Instituto Clavel the extensive experience of our team of neurosurgeons, and use of the latest technology, allows us to perform shunting procedures successfully in the vast majority of cases, and to solve any problems that might occur in relation to it .
This operation is performed by the following neurosurgeons:
Contact us so that we can give you a personalized assessment.